In an era dominated by instant messaging apps and social media platforms, it’s easy to overlook the humble yet powerful SMS (Short Message Service). sms gateway, the bedrock of mobile communication, continues to play a vital role in connecting individuals and businesses worldwide. Behind the scenes of this seemingly simple service lies a sophisticated infrastructure known as the SMS gateway, a pivotal component facilitating seamless communication across diverse networks.
Understanding the SMS Gateway
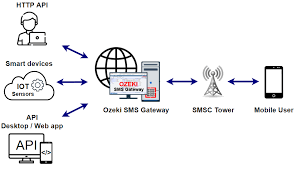
At its core, an SMS gateway is a telecommunications network node or service that allows the sending and receiving of SMS messages between different communication devices, such as mobile phones, computers, or other telecommunication systems. It serves as a bridge between the world of mobile carriers and the digital realm, enabling messages to traverse between different protocols and formats.
How SMS Gateways Work
The process of sending an SMS message involves several steps orchestrated by the SMS gateway:
- Message Origination: The journey begins when a user initiates a message from their device. Whether it’s a simple text or a more complex transactional notification, the message is formatted and transmitted to the SMS gateway.
- Routing and Conversion: Upon receiving the message, the SMS gateway analyzes the destination number and selects the appropriate route for delivery. This might involve converting the message into a format compatible with the recipient’s network or language.
- Carrier Interaction: The gateway interacts with the recipient’s mobile carrier to determine the most efficient delivery path. This process often involves negotiating with multiple carriers to ensure reliable and timely delivery.
- Delivery Confirmation: Once the message reaches its destination, the SMS gateway receives confirmation from the recipient’s carrier and notifies the sender of successful delivery. This feedback loop is crucial for ensuring message integrity and reliability.
Applications of SMS Gateways
The versatility of SMS gateways makes them indispensable across a wide range of applications:
- Business Communication: From marketing campaigns to customer support, businesses leverage SMS gateways to reach customers directly on their mobile devices. Automated messaging systems can send appointment reminders, delivery notifications, or promotional offers, enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Authentication and Security: SMS gateways play a vital role in two-factor authentication (2FA) and verification processes. By sending one-time passwords (OTPs) or verification codes via SMS, organizations add an extra layer of security to their online services, protecting users from unauthorized access.
- Alerting and Notifications: Emergency alerts, service outages, or critical updates can be disseminated quickly and efficiently through SMS gateways. Government agencies, healthcare providers, and enterprises rely on this instant communication channel to keep stakeholders informed in real-time.
- Integration with Software Platforms: SMS gateways often integrate seamlessly with existing software platforms, enabling developers to incorporate SMS functionality into their applications. Whether it’s a CRM system, e-commerce platform, or IoT device, SMS gateways provide a reliable means of communication.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their ubiquity and reliability, SMS gateways face certain challenges and considerations:
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with telecommunications regulations and privacy laws is essential to avoid legal complications. SMS gateways must adhere to guidelines regarding message content, sender identification, and user consent to ensure ethical and lawful operation.
- Network Reliability: While SMS is known for its robustness, occasional network congestion or outages can disrupt message delivery. SMS gateways employ redundant infrastructure and failover mechanisms to mitigate the impact of network disruptions.
- Security Concerns: SMS-based communication is susceptible to interception or spoofing, posing security risks for sensitive information. Implementing encryption protocols and authentication mechanisms can enhance the security of SMS transmissions.
- Scalability and Performance: As messaging volumes increase, SMS gateways must scale dynamically to handle the load efficiently. Performance optimization and resource management are critical to maintaining responsiveness and reliability.
Looking Ahead
As technology continues to evolve, the role of SMS gateways in the digital ecosystem remains ever-relevant. Whether facilitating business transactions, disseminating critical information, or strengthening security measures, SMS gateways serve as the linchpin of mobile communication infrastructure. By embracing innovation and addressing emerging challenges, SMS gateways will continue to empower connectivity and foster communication in an increasingly interconnected world.